It was cubism that created a revolution in painting and sculpture in the early twentieth century. The movement did not last long and has a great resonance in contemporary time, but it has become the basis for a great creative explosion throughout the flow of painting of the century.
What is Cubism?
Cubism has been considered to be one of the most influential visual art schools of the 20th century, founded by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque in Paris from 1907 to 1920. The cubist style emphasizes on the 2D plane, eliminating the traditional expression of perspective and the art theory which favor the natural imitation. They are not bound to the shape, surface structure, color or space. Instead, they bring to viewers a new form of reality through artworks depicting objects divided into multiple arrays and expressed from multiple angles.
Characteristics & Style of Cubism Art
Cubism appeared when the artist was looking for an approach that expresses the natural world in a new way, helps them reflect things beyond the ordinary appearance of the matter. The cubist artist represents objects from different angles simultaneously. Thus, the form of the object is also broken down into areas, arrays, and geometric shapes. It can be said that the Cubist artists see things in a parallel way in space and time.
The development of Cubism can be divided into three stages: Cubism influenced by Cézanne (1907 – 1909); Analytical Cubism (1909 – 1912) and Synthetic Cubism (1912 – 1914). Most of the artists follow Cubism have composed in both analytical and synthesized styles.
Analytical Cubism
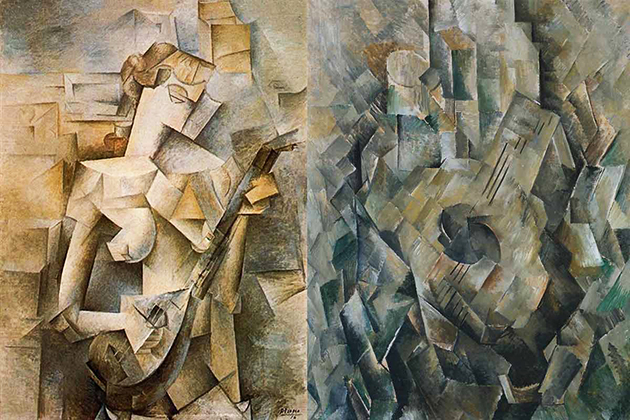
Analytical cubism is characterized by the discrete appearance of many viewpoints and overlapping planes. It is termed analytical cubism due to the structured dissection of the subject from different angles, which leads to the complexity of the picture. Objects in the painting are divided into many small, confused, and quite abstract arrays. The small patches are densely put at the center and then spread out in many directions, toward the edges. Another feature of this style is that the color scheme is so simple that it’s almost monochrome. In this period, painters use almost the same color palette, in favor of yellow and brownish-grey color.
Synthetic Cubism
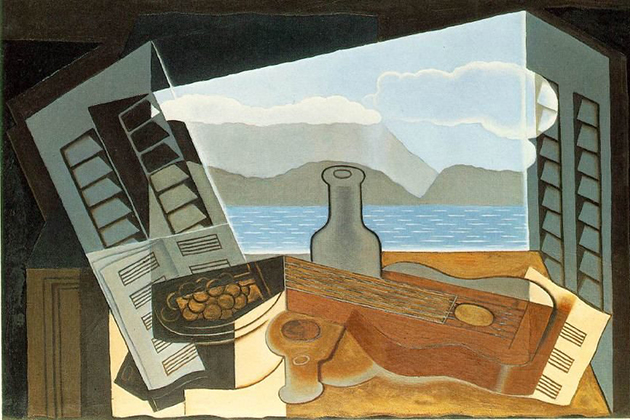
Synthetic Cubism goes against the layout principle of Analytical Cubism. In the Synthetic Cubism, the layout of the painting consists of overlapping details, which are painted onto the canvas. Instead of breaking the object into small pieces and then reassembling, the image in this style is built from new elements and shapes. The main features of the Synthetic Cubism are summarized as follows: simple lines and shapes, brilliant colors with many basic colors such as red, yellow, orange, blue,…
This period also marked the birth of paper painting. It was Picasso who invented the paper painting with his famous painting “The Still Life With A Cloud”, in which he pasted the oilcloth on a piece of the rattan chair. Braque also inspired this painting to create “The Fruit Plate and the Glass”. The surface structure is also an interest when artists can make use of paper materials along with the paint.
The Outstanding Artists of Cubism
Pablo Picasso (1881 – 1973)
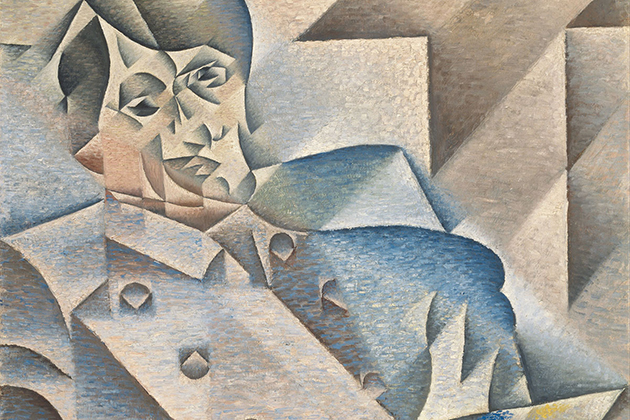
Pablo Picasso, the leader of the Cubism, was a special phenomenon of early 20th – century painting. In the early stages of painting, as well as many other artists, the expression of Picasso in painting was very close to the visual sense of reality despite having the potential for innovation. Before finding out the Cubism, he experimented on composing through a number of different schools of art. Then, the influences from the style of Henri Matisse and Henri “Le Douanier” Rousseau as simple drawings, as well as the inspiration derived from Iberian sculpture, Africa sculpture, and Gauguin’s artworks were harmonized by Picasso to become a preliminary material for Cubist painting.
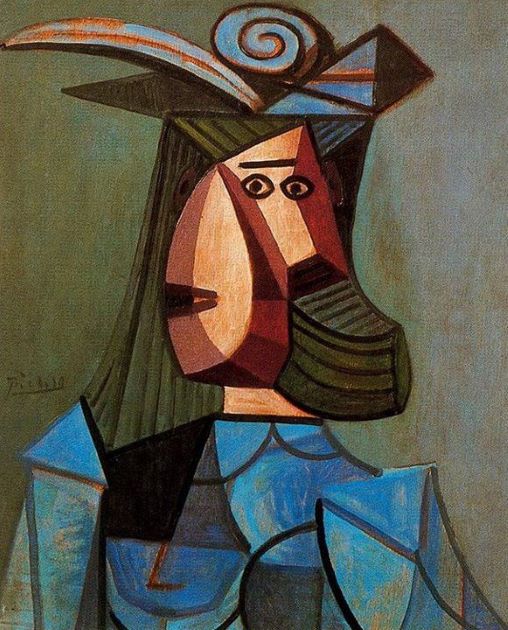
The artwork “Avignon girls” by Picasso composed in 1907 officially marked the emergence of Cubism. In this painting, Picasso processed the cubes by analyzing them into more rough, strong, and non-conventional views. The most striking feature of Picasso’s Cubism conception is in the facial expressions of girls in the picture, which is distorted and difficult to determine which direction they are facing. At the same time, the character formation method clearly shows the influence of African art.
Among the topics of works by Spanish artists, we can see the image of the women who had appeared in his life. Picasso’s cubist artworks on women are always very special. They always have something intricate, distorted, and even scary. In addition, he also expressed the social tendency in his compositions with the thorny and intense expression about burning issues such as war or the human condition.
Georges Braque (1882-1963)
Georges Braque was a self-taught artist but became successful very soon. He was the one who invented the paper-sticking technique, making paintings by drawing wood or marble grain in modern art. Unlike Picasso, Braque’s style is homogeneous. In Braque’s artworks, people most find only arrays of dark brown, gold, reddish-brown or grey colors but can hardly find brilliant colors.
In Analysis Cubism, Braque divided the cubes into rectangles, triangles,… superimposed on each other. Colors are reduced to the minimum of their expressiveness, leaving only a gray-brown tone. In Synthetic Cubism, Braque particularly liked to put the prints and stick the newspaper on the surface of the painting. The newspaper material appears very real next to the blurry or a little bit of abstract image.