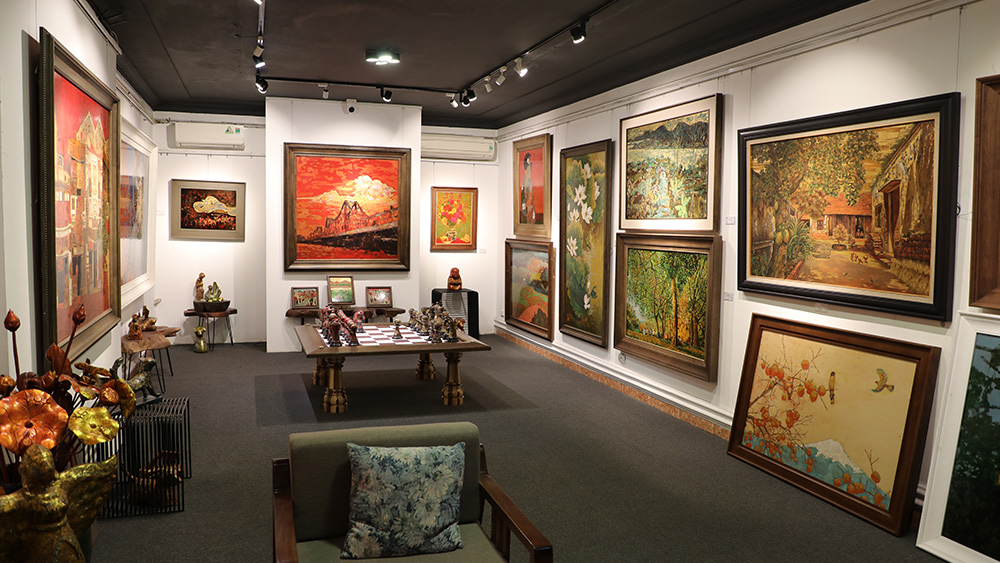
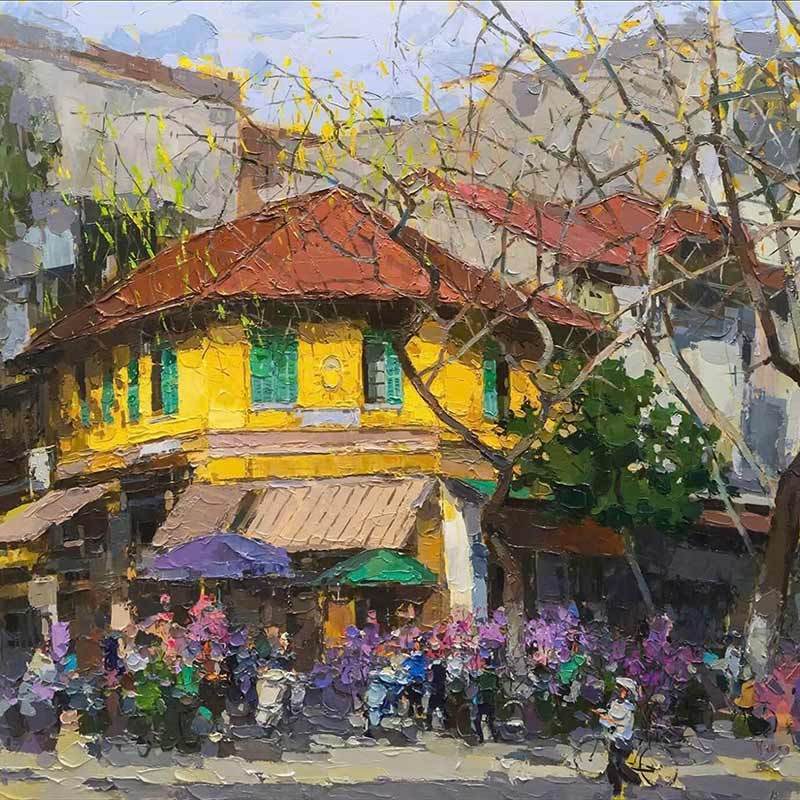
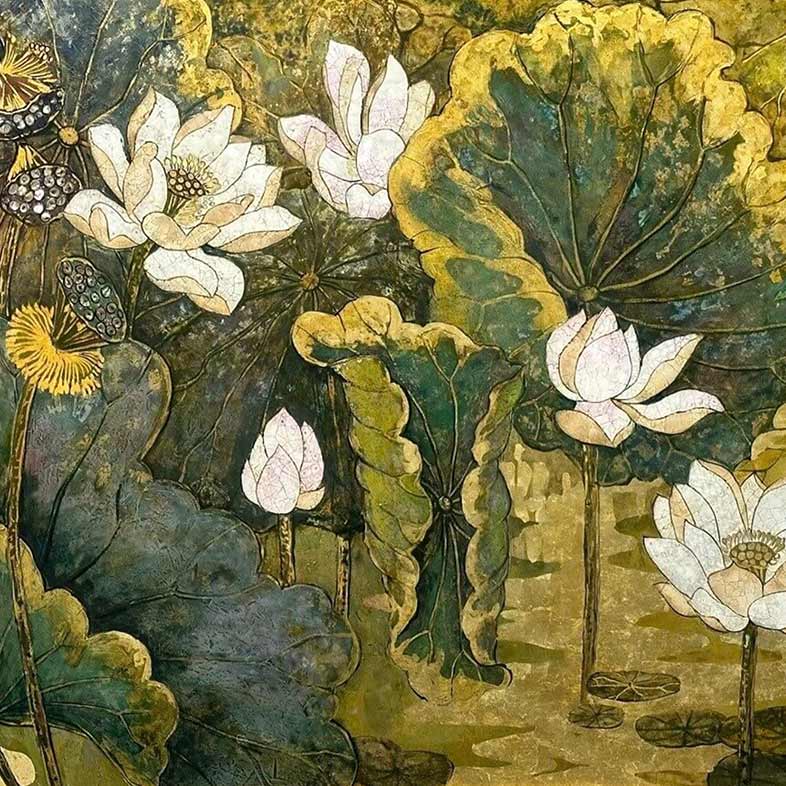
Vietnamese painting has a rich and vibrant history that spans over a thousand years. The earliest known Vietnamese paintings were produced during the Dong Son culture, which existed from around 700 BC to AD 100. These paintings depicted daily life scenes, as well as religious and mythological subjects.
During the Ly and Tran dynasties (11th to 14th centuries), Vietnamese painting flourished, with the development of genres such as landscape, portrait, and still life. Buddhist themes also became prominent during this period.
In the 15th century, Chinese influence on Vietnamese painting increased, particularly in the use of ink and brush techniques.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw the development of different schools of painting in Vietnam, including the Hue School, which was known for its use of bold colors and detailed brushwork, and the Hanoi School, which was more influenced by French Impressionism.
In the 20th century, Vietnamese painting continued to evolve, with artists experimenting with different styles and techniques.